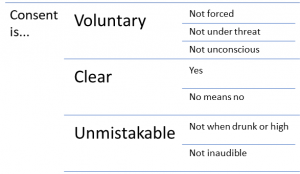
If you find out that child sexual abuse is taking place, you must report it to the police, who in turn must record your complaint in writing. If you are aware of any incident and are reasonably certain that a child is a victim of any form of sexual abuse happening to a child during the pandemic please use any of the mentioned ways to contact an authority to help the child out.
Online:
The government has an online complaint system where you can file your complaint. Your complaint will be filed to the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights.
Phone:
You can contact the following numbers:
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights- 9868235077
Childline India (Childline is a helpline for offences committed against children)- 1098
Email:
You can send an email to National Commission for Protection of Child Rights: pocsoebox-ncpcr@gov.in
Police:
Call 100 to contact the police about any information you have about any incident of child sexual abuse. After you complain, the child will be taken care of by the local police/Special Juvenile Police who will inform the Child Welfare Committee of your district who will further appoint a Support Person to assist the child and the family of the child in the legal process that will follow after the complaint.
Mobile App:
You can download the mobile app called the POCSO e-box (Android users only) and report the abuse directly through it.
Post/Letter/Messenger:
You can write to the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights with your complaint or send a messenger to this address: National Commission For Protection Of Child Rights (Ncpcr), 5th Floor,Chandralok Building 36, Janpath, New Delhi-110001 India.