Yes, you can file an FIR against your husband if he rapes you or tries to have sex with you forcefully, while you are separated. He will be punished with jail time anywhere between seven years and life imprisonment, along with a fine.(( Section 376 B, Indian Penal Code, 1860.))
Theme: Rape
Can a woman believe that a random man is her husband and give consent for sex? Is this rape?
Sometimes a woman may be duped into believing that a random man may be the husband due to darkness or the woman not being in a good state of mind. This is a form of cheating by men and punishable under the law.
If someone forcefully removes my clothes is it rape?
No, it is not rape. If a man assaults a woman in order to remove her clothes or to force her to be naked, he can be punished for the crime of disrobing(( Section 354B, Indian Penal Code, 1860.)). The punishment for attempting to disrobe, or actually disrobing a woman, is imprisonment from three to seven years, along with a fine(( Section 354B, Indian Penal Code, 1860.)).
I am a reporter, can I publish the name of the survivor in my report?
No you cannot publish the name of the survivor. The name and identity of the survivors are protected by the law and it is an offence to publish the name of the survivor.
Can a woman be charged with rape?
No, only a man can be charged with rape.
I am an 18 year old guy and in a relationship with a girl who is 17 years old. Will it be rape if we have consensual sex?
Yes, it will be rape because she is below eighteen years old.
I have been married for 5 years and my wife is above 18 years old. If I force her to have sex with me, will it lead to rape?
No, because she is above eighteen years old. However, you can be prosecuted for other charges such as harassment and domestic violence.
What is Rape?
[Trigger Warning: The following content contains information on physical violence and sexual violence which some readers may find disturbing.]
Rape is a crime that occurs when a man has sexual intercourse with a woman against her will or without her consent.
A man commits rape on an non-consenting woman if he:((Section 63, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023))
- penetrates his penis or inserts any other part of his body (to any extent) into the woman’s vagina, mouth, urethra, or anus, or forces her to do this with him or another person; or
- inserts any object into the woman’s vagina, mouth, urethra, or anus, or forces her to do this with him or another person; or
- manipulates any part of the body of a woman to cause penetration into the woman’s vagina, urethra, anus, or any part of the body or makes her to do so with him or any other person; or
- applies his mouth to the woman’s vagina, anus, or urethra, or makes her do this with him or any other person.
A medical procedure or intervention is not considered as rape. For example, if a doctor examines the private parts of a patient as part of a medical procedure, this is not rape.
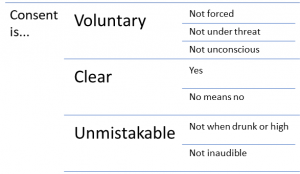
What is Consent?
Consent is a voluntary, clear, and unmistakable agreement by a person who expresses their willingness to take part in a specific sexual act. A woman should understand what she is agreeing to and what the consequences will be if she agrees to the sexual activity. Even if she doesn’t physically resist the act of penetration, this does not automatically mean that she has consented to the sexual activity.
Under the following circumstances, a man is said to commit rape even if the woman has given her consent:
- If her consent has been forcibly obtained by threatening to hurt her or making her fear for her life or the lives of her dear ones.
- If the man knows that he is not a woman’s husband and that she has given her consent only because she thinks that the man is her husband.
- If the woman is unable to understand the nature and consequences of the act to which she gives consent, due to unsoundness of mind or intoxication or because the man has given her an unwholesome substance.
- If the woman is under eighteen years of age.
Consent of a minor
Sex with a girl who is below eighteen years of age (a minor) is considered rape, even if the girl consents to have sex.
For example, if a man has sex with a seventeen-year-old girl, it is considered rape, even if the girl agrees to have sex.
Punishment for Rape
[Trigger Warning: The following content contains information on physical violence and sexual violence which some readers may find disturbing.]
The punishment for rape is imprisonment for ten years to life imprisonment, along with a fine.1
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) provides for two types of imprisonment: simple imprisonment and rigorous imprisonment. Rigorous imprisonment is a harsher punishment than simple imprisonment, involving hard labor, and is usually reserved for serious crimes.
The punishment is more severe in the following circumstances:
When the survivor is below sixteen years
When the survivor is below sixteen years, the punishment is imprisonment for twenty years to life imprisonment (imprisonment for the rest of the person’s natural life), along with a fine.2
If the survivor is below twelve years old, the perpetrator can also be given the death penalty.3 The fine should be just and reasonable to meet the medical expenses and rehabilitation of the survivor and is paid to the survivor.
When rape results in a woman’s death or vegetative state
If rape results in an injury that causes the death of the woman or puts her in a persistent vegetative state, the perpetrator is punishable with imprisonment for twenty years to life imprisonment (imprisonment for the rest of the person’s life), along with fine or with death.4
What is Gang Rape?
[Trigger Warning: The following content contains information on physical violence and sexual violence which some readers may find disturbing.]
Gang rape refers to the rape of a woman by multiple people/a group of people acting together with the common intention to rape. In a case of gang rape, each person in the group is guilty of the crime.1
The punishment for gang rape is rigorous imprisonment for twenty years to imprisonment for the rest of the perpetrator’s natural life and fine.2
If the survivor is below eighteen years, the punishment is life imprisonment for the rest of the perpetrator’s life along with fine, or death.
Further, the perpetrators must pay a fine that is just and reasonable to meet the medical expenses and rehabilitation of the survivor. The fine is paid to the survivor.
Punishment for Repeating the Crime
If someone has been previously held guilty for the crime of rape/gang rape, and they are subsequently held guilty for rape/gang rape again, they are punishable with life imprisonment (imprisonment for the remainder of that person’s natural life) or death.1
- Section 71, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
Marital Rape
[Trigger Warning: The following content contains information on physical violence and sexual violence which some readers may find disturbing.]
Marital rape is not a crime under Indian law. The law does not punish a husband for having forcible sexual intercourse with his wife without her consent unless she is below eighteen years of age (a minor). (( Independent Thought v. Union of India, (2017) 10 SCC 800))
So, any sexual intercourse or sexual acts by a man with his adult wife is not rape. However, this does not apply if a woman is living separately from her husband. If a couple is married, but living separately, then the husband is guilty of rape if his wife does not consent to sexual intercourse. In this case, the punishment for the husband is imprisonment between two and seven years, along with a fine.1
Though the law does not punish marital rape, a woman can get relief under the Domestic Violence Act, 2005. This law criminalises sexual abuse, including any behaviour of a sexual nature that abuses, humiliates, degrades or violates the dignity of a woman.2 To know more about the rights of a woman against domestic violence, read here.

Abuse of Position or Authority
[Trigger Warning: The following content contains information on physical violence and sexual violence which some readers may find disturbing.]
If a man has control over a woman because of his job or position and uses this control to make a woman have sex with him, it is a crime.1 The law provides punishment for any person who abuses his position or fiduciary relationship (relationship of trust) to convince or seduce any woman to have sexual intercourse with him. The woman could be in his custody, under his charge, or present on the premises. Here, sexual intercourse does not refer to the act of rape and is dealt with as a separate offence under Section 63 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita.
The person who persuades the woman to have sexual intercourse could be:
- in a position of authority or in a fiduciary relationship; or
- a public servant; or
- superintendent or manager of a jail, remand home, other place of custody, or a women’s or children’s institution; or
- on the management or staff of a hospital.
- a relative, guardian, or teacher.
In these cases, the person in authority is punishable with imprisonment for five to ten years, along with a fine.
For example, if a male jail superintendent asks a female prisoner to have sex with him in return for supporting her release, and thus convinces her to have sex with him, he is abusing his position. In this case, he has not forced himself on her and committed rape but convinced her to have sex with him by using his position of power.
- Section 68, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
Reporting Rape
Police
- If an offense of rape is committed, the first and most important thing to do is to report it to the police by filing a First Information Report (FIR).1 Otherwise, call 1091 (Women’s Helpline Number) and report the rape.
Even if someone does not report the crime right away, this does not mean that the delayed FIR will harm the case. It may become more difficult for the police to carry out the investigation and gather evidence, but it is possible to file an FIR at a later date as well. - To file an FIR, visit the nearest police station. The police station does not necessarily have to be in the area where the crime has been committed. To locate the police station, download the ‘Indian Police at your Call’ app and locate the nearest police station. Otherwise, call 100.
- Approaching the police immediately after being assaulted can be very daunting for the survivor. However, the survivor doesn’t have to do this alone. The woman can take the help of a friend or approach a lawyer to assist her in filing a complaint. In fact, another person can file the FIR for the woman if she doesn’t want to approach the police by herself.2
If the survivor approaches the police with her complaint, the information is recorded only by a woman officer. - If the survivor is physically or mentally disabled, the police come and take her complaint from her residence or any other place where she feels comfortable.3 The survivor’s statement is recorded at her residence or in any place of her choice. As far as possible, the statement is recorded by a woman police officer in the presence of the survivor’s parents/guardian/near relatives/ social worker of the locality.4
- It is perfectly alright if the survivor does not remember specific details of the assault or even the attacker. It is enough if she tells the police as many details as she remembers.
- Once the police have read out the complaint, if all the details are correct, the complainant signs the FIR.5 If any police officer refuses to file the FIR or fails to record information of the offence the substance of the information in writing and by post is to be shared with the Superintendent of Police, who can further investigate the case himself or direct an investigation to be made, if he fails to do so the aggrieved person may make an application to the Magistrate.6
- The complainant can get a copy of the FIR for free.7 It is also possible to freely access the FIR online using the FIR number, date of FIR, and the name of the police station.
- After the FIR has been registered, the contents of it cannot be changed. However, additional information can be given to the police later on at any point.
One Stop Centres
A survivor can also approach One Stop Centres, which provide an integrated range of services to women affected by violence. These services include medical aid, police assistance, legal aid/case management, psychosocial counseling, and temporary support services.
- Section 193, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Hallu and Others v State of Madhya Pradesh, 1974 AIR 1936 [↩]
- Section 173(4), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 176, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 173(3), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 173(4),Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 173(2), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
Seeking Medical Help
Survivors have the right to get immediate and free first-aid or medical treatment from medical institutions (both public and private). The institution must also inform the police of the criminal incident.1 If the institution refuses to provide treatment and inform the police, the person in charge of the institution is punishable with imprisonment for up to one year and/or a fine.2
Within 24 hours of receiving information about the criminal incident, the police send the survivor to an authorized doctor for a medical examination. The medical examination can happen only with the consent of the survivor or someone who can consent on her behalf.3 After obtaining consent, the doctor immediately examines the survivor and prepares a detailed report with conclusions about the survivor’s injuries, mental condition, etc.4 The report also records that consent was obtained, and notes the exact time at which the medical examination was started and completed.5 The registered medical practitioner shall, within a period of seven days forward the report to the investigating officer who shall forward it to the Magistrate.6
- Section 190(3), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 200, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 184(4), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 184(2), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 184(5), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
- Section 184(6), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 [↩]
Protecting the Identity of the Survivor
No one is allowed to print or publish the name or any matter which may reveal the identity of a survivor. The punishment for doing so is imprisonment for up to two years and a fine.1 Without getting permission from the court, if anyone prints or publishes any matter about a rape case which is currently ongoing in court, they are punishable with imprisonment for up to two years and a fine.2
The identity of the survivor can only be revealed:3
- For the purposes of investigation – In this case, the identity can be revealed by the officer-in-charge of a police station or the police officer investigating the case.
- By the survivor, or with her written permission.
- By the close family of the survivor, or with their permission – This is allowed if the woman is dead, or a minor, or of unsound mind. In this case, the family can give such permission only to the chairman or the secretary of any recognised welfare institution or organisation.
Rape Trial
The inquiry and trial of a rape offence are conducted in camera i.e., not open to the public. However, the judge may allow a person to access or observe the court trial if one of the parties makes an application for the same. As far as possible, the trial is conducted by a woman judge.1
In certain cases of rape, where sexual intercourse is proved and the survivor says she did not consent, the court legally assumes that the survivor did not consent.2 Then, it is up to the accused person’s lawyer to prove, if possible, that the survivor actually consented and the sexual intercourse was consensual and not in the nature of rape.
The inquiry or trial is completed within two months from the date of filing the chargesheet.3